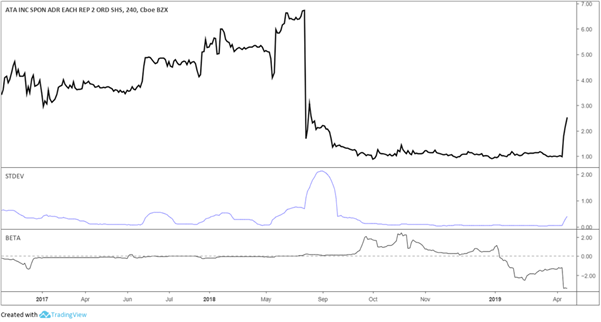
Low volatility is a major source of frustration among many traders as the amount of opportunity to trade – or should I say, make ‘good’ trades – diminishes. Frustration generally only breeds one thing – more frustration. We can’t control how the market behaves just as we can’t control the outcome of our trades, but what we can control is how we react and conduct ourselves.
Volatility ebbs from low to high and back again, across all time-frames. In that statement lies the silver lining; when volatility is low, look at it like this – it will pick back up again (and maybe soon). But until it does we need to accept what the market is providing. It is imperative to lower expectations so as to protect both trading and mental capital (always want to keep your head as clear as possible). To combat uneasiness which can arise by the lack of opportunity, be mindful and think – For every loss I avoid, it’s one less loss I have to make back when volatility or optimal trading conditions return…” And, again, volatility will return.
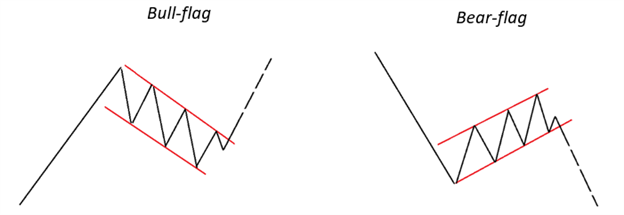
We examined (again) the simple concept of using a checklist, whether it be a physical one (i.e. spreadsheet) or a mental one (which seasoned traders are likely to use). A checklist includes various criteria such as risk management parameters and criteria needed for a trade set-up. Like volatility, your trading activity and performance won’t be evenly distributed; there will be times where set-ups appear frequently and other times when they don’t.
When the market is ‘dull’ there are things we can do to still be productive; study trade history/review journal entries, read books/websites, listen to and read what seasoned traders have to say, and even – relax! You have to trust that a good trade or better environment is around the corner. So, at the end of the day, if a proper mentality is adopted, one not need to become frustrated.
more...


 LinkBack URL
LinkBack URL About LinkBacks
About LinkBacks





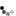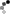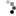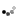
 Reply With Quote
Reply With Quote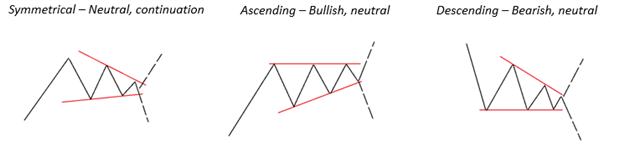

Bookmarks